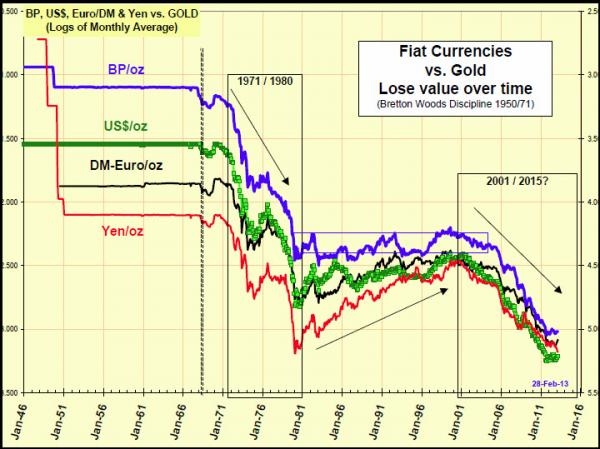
Curiously, many people argue this would be a good time to abandon gold. We don’t think so – we rather think that faith in central banks will eventually crumble, and then it will be well and truly ‘game over’ for these perpetual bubble machines. As a friend of ours frequently remarks: at that point the question of how to price gold will be akin to asking what the last functioning parachute on an airplane that is going down should be worth. http://www.acting-man.com/?p=23082
—
Hedge fund “friend” upon hearing that I own gold, “If you were a lot smarter, we could call you stupid.”
Why Gold?
No, I am not actually doing what I posted here:http://wp.me/p2OaYY-1Vv. I own gold bullion and several precious metals miners, so yesterday when the stock market is up 1/2% while my portfolio drops 1%+, I take comfort when I review why I own gold:
“In a speech in Rome, ECB President Mario Draghi said the bank would monitor incoming data closely and be ready to cut rates further, including the deposit rate currently at zero.
“For southern European countries, a euro above $1.30 would be too high for their economy. Among major central banks, the ECB has been the only bank that is not expanding its balance sheet. But It will likely consider such a step,” said Minori Uchida, chief FX analyst at the Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ.”
Meanwhile, sentiment in gold and precious metals miners is at historic (20 year) lows: http://thetsitrader.blogspot.com/2013/05/gold-and-silver-sentiment-reversal-is.html and Short Side of Long
While……..China and other Asian countries buy on dips.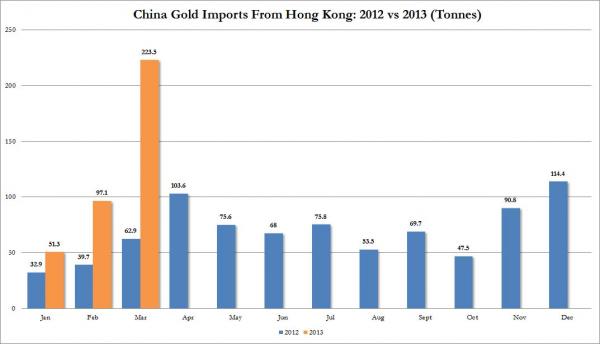
I don’t buy the gold bugs premise that central banks will back their currencies with gold unless forced to by the market/the public. However, central bankers buying may indicate the lack of trust in their colleagues’ fiat currencies. Also, gold “flowing” East represents a wealth transfer from West to East.
Print, print: http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2013-05-08/germany-under-pressure-create-money
In The Wilderness by Paul Singer
[T]he financial system (including the institutions themselves, products traded, and risks taken) has “gotten away from” the Fed’s ability to comprehend. The Fed is primarily responsible for that state of affairs, and it is out of its depth. Former Chairman Greenspan created — and reveled in — a cult of personality centered on himself, and in the process created a tremendous and growing moral hazard. By successive bailouts and purporting to understand (to a higher and higher level of expressed confidence) a quickly changing financial system of growing complexity and leverage, he cultivated an ever-increasing (but unjustified) faith in the Fed’s apparent ability to fine-tune the American (and, by extension, the world’s) economy. Ironically, this development was occurring at the very time that financial innovations and leverage were making the system more brittle and less safe. He extolled the virtues of derivatives and minimized the danger of leverage and risky securities and dot-com stocks, all while he should have been putting on the brakes. It was not just the disappearance of vast swaths of the American financial system into unregulated subsidiaries of financial institutions, nor was it just government policies that encouraged the creation and syndication of “no-documentation” mortgages to people who could not afford them. It was also the low interest rates from 2002 to 2005, the failure to see the expanding real estate bubble caused by an unprecedented increase in leverage and risk, and the general failure to understand the financial conditions of the world’s major institutions.
Under Chairman Bernanke, the combination of ZIRP and QE completed the passage of the Fed from sober protector of a fiat currency to ineffective collection of frantically-flailing, over-educated, posturing bureaucrats engaged in ever more-astounding experiments in monetary extremism.
If you look at the history of Fed policy from Greenspan to Bernanke,you see two broad and destructive paths quite clearly. One path is the cult of central banking, in which the central bank gradually acquired the mantle of all-knowing guru and maestro, capable of fine-tuning the global economy and financial system, despite their infinite complexity. On this path traveled arrogance, carelessness and a rigid and narrow orthodoxy substituting for an open-minded quest to understand exactly what the modern financial system actually is and how it really works. The second path is one of lower and lower discipline, less and less conservative stewardship of the precious confidence that is all that stands between fiat currency and monetary ruin.
Monetary debasement in its chronic form erodes people’s savings. In its acute and later stages, it can destroy the social cohesion of a society as wealth is stolen and/or created not by ideas, effort and leadership, but rather by the wild swings of asset prices engendered by the loss of any anchor to enduring value. In that phase, wealth and credit assets (debt) are confiscated or devalued by various means, including inflation and taxation, or by changes to laws relating to the rights of asset holders. Speculators win, savers are destroyed, and the ties that bind either fray or rip. We see no signs that our leaders possess the understanding, courage or discipline to avoid this.
It is true that the CEOs of the world’s major financial institutions lost their bearings and were mostly oblivious to their own risks in the years leading up to the crash. However, as the 2007 minutes make clear, the Fed was clueless about how vulnerable, interconnected and subject to contagion the system was. It is not the case that the Fed completely ignored risk; indeed, several Fed folks made “fig leaf” statements about the risks of the mortgage securitization markets, as well as other indications that they appreciated the possibility of multiple outcomes. But nobody at the Fed understood the big picture or had the courage to shift into emergency mode and make hard decisions. In the run-up to the crisis the Fed was a group of highly educated folks who lacked an understanding of modern finance. After convincing the nation for decades of their exquisite grasp of complexities and their wise stewardship of the financial system, they didn’t understand what was actually going on when it really counted.
Ultimately, of course, as the system was collapsing and on the verge of freezing up completely, the Fed shifted into the (more comfortable and much less difficult) role of emergency provider of liquidity and guarantees.
All this background presents an interesting framework in which to think about what the Fed is doing now. QE is a very high-risk policy, seemingly devoid of immediate negative consequences but ripe with real chances of causing severe inflation, sharp drops in stock and bond prices, the collapse of financial institutions and/or abrupt changes in currency rates and economic conditions at some point in the unpredictable future. However, the lack of large increases in consumer price inflation so far, plus the demonstrable “benefits” of rising stock and bond markets, have reinforced the merits of money-printing, which is now in full swing across the world. In the absence of meaningful reforms to tax, labor, regulatory, trade, educational and other policies that could generate sustainable growth, “money-printing growth” is unsound.We believe that the global central bankers, led by the Fed as “thought leader,” have no idea how much pain the world’s economy may endure when they begin the still-undetermined and never-before attempted process of ending this gigantic experimental policy. If they follow the paths of the worst central banks in history, they will adopt the “tiger by the tail” approach (keep printing even as inflation accelerates) and ultimately destroy the value of money and savings while uprooting the basic stability of their societies. Read the 2007 Fed minutes and you will understand how disquieting is the possibility of such outcomes and how prosaic and limited are the people in whom we have all put our trust regarding the management of the financial system and the plumbing of the world’s economy.
Printing money by the trillions of dollars has had the predictable effect of raising the prices of stocks and bonds and thus reducing the cost of servicing government debt. It also has produced second-order effects, such as inflating the prices of commodities, art and other high-end assets purchased by financiers and investors. But it is like an addictive drug, and we have a hard time imagining the slowing or stopping of QE without large adverse impacts on the prices of stocks and bonds and the performance of the economy. If the economy does not shift into sustainable high-growth mode as a result of QE, then the exit from QE is somewhere on the continuum between problematic and impossible.
Central banks facing high inflation and/or sluggish growth after sustained money-printing frequently are paralyzed by the enormity of their mistake, or they are deranged by the thought that the difficult and complicated conditions in a more advanced stage of a period of monetary debasement are due to just not printing enough. At some stage, central banks inevitably realize, regardless of whether they admit the catastrophic nature of their own failings, that the cessation of money-printing will cause an instant depression. Even though at that point the cessation of money-printing may be the only action capable of saving society, that becomes a secondary consideration compared to the desire to avoid immediate pain and blame. The world’s central banks are in very deep with QE at present, and the risks continue to build with every new purchase of stocks and bonds with newly-printed money.
* * *
[And, as an added bonus, here are Singer’s views on gold:]
There are many current theories as to why the price of gold had been drifting down and then collapsed in mid-April. We are trying to sort out various possible explanations, but we urge investors to be cautious in their thinking about what circumstances would likely cause gold to rise or fall sharply. The correlations with other assets in various scenarios (risk on or off, economic normalization, inflation, the rise and fall of interest rates, euro collapse) may shift abruptly as the macro picture evolves. Many people think that if stock markets continue rising, and/or if the U.S. and Europe restore normal levels of growth and employment, then the rationale for owning gold is weakened or destroyed. This perception may be correct, and it is certainly a topic that is currently much discussed, but ultimately another set of considerations is likely to dominate.
The world is on a seemingly one-way trip to monetary debasement as the catchall economic policy, and there is only one store of value and medium of exchange that has stood the test of time as “real money”: gold. We expect this dynamic to assert itself in a large way at some point. In the meantime, it is quite frustrating to watch the price of gold fall as the conditions that should cause it to appreciate seem more and more prevalent. Gold may not exactly be a “safe haven” in the sense of an asset whose value is precisely known and stable. But it surely is an asset that, in a particular set of circumstances, becomes a unique and irreplaceable “must-have.” In those circumstances (loss of confidence in governments and paper money), there are no substitutes, and the price of gold may reflect that characteristic at some point.
—
Disprove Your Opinions on Gold
By Bobnoxy
This review is from: Gold Bubble: Profiting From Gold’s Impending Collapse (Hardcover)
This book will no doubt go into the proverbial dustbin of history along with Dow 36,000. Ask yourself some honest questions and then compare your answers to this book’s entire premise.
Is gold in a bubble? Well, what do bubbles look like? Luckily, we have two recent examples, the housing bubble, and the tech stock bubble in the late 90’s. What did those look like?
To me, they looked like everyone was getting rich in techs stocks and flipping houses. Regular people were quitting their jobs and day trading or flipping houses full time. The average guy, the little guy, sometimes referred to as the ”dumb money” was making an easy fortune.
Now, how many of your friends own any gold and talk about it with you? How much do you own? The writer points to all the publicity around gold, like those ads telling people to sell their gold. And ever since gold hit $1,000, people were doing just that, selling their gold.
In a bubble, those people would be loading up, but they’re selling! The world’s central banks, the smartest people in the world when it comes to money, are the big buyers. This would be the first bubble in history that the dumb money was selling into and the smartest money on the planet was buying. Do you really think that the people with the least knowledge about money are getting this right?
It would also be the first bubble to happen with almost no participation from the general public. This could be the weakest analytical book written this year. Just because the price of something is up does not mean it’s in a bubble.
If you look at the average selling price of gold in the year it peaked for the last bull cycle, 1980, or $660 an ounce, and look at today’s price, the average annual gain for that 32 years is about 3%. If stocks had risen by 3% annually for that long, would anyone be calling it a bubble?
Then look at our trillion dollar deficits and the growth in the Fed’s balance sheet, total government debt of $18.5 trillion when you include state and local debt that as taxpayers, we’re all on the hook for, and there’s your bubble, and the best reason to defend yourself by owning gold.
Readings:
Thanks to a reader’s contribution: Here is a good article attached on bureaucracy and leading to misguided incentives. http://www.nytimes.com/2013/05/12/magazine/the-food-truck-business-stinks.html?ref=magazine&pagewanted=print
Another reader:
I came across your website via your interview with Classic Value Investors. I like the way you try to help people learn the craft. Value investing is in principle not that difficult, as long as you have a good teacher. So well done!
On my own value investing blog (http://www.valuespreadsheet.com/value-investing-blog). I try to share my knowledge on the subject as well, but not per sé with case studies like you do. However, your approach is very informative for readers, so maybe I should try that some more.
I’ve also written a free eBook which explains three valuation models in simple words. Feel free to add it to your value investing resources if you like it:
http://www.scribd.com/doc/137908826/How-to-Value-Stocks-By-Value-Spreadsheet
Kind regards, Nick Kraakman, www.valuespreadsheet.com
—-
Thanks for the above contributions.