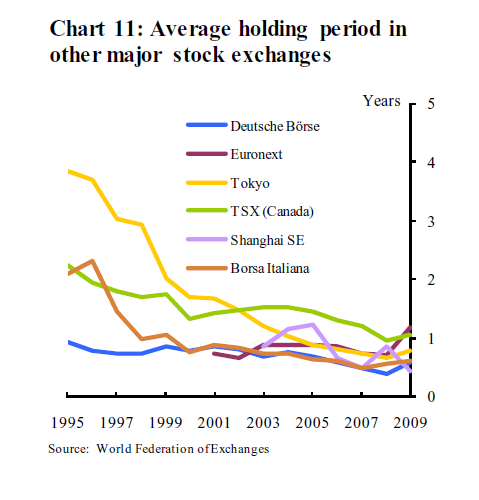
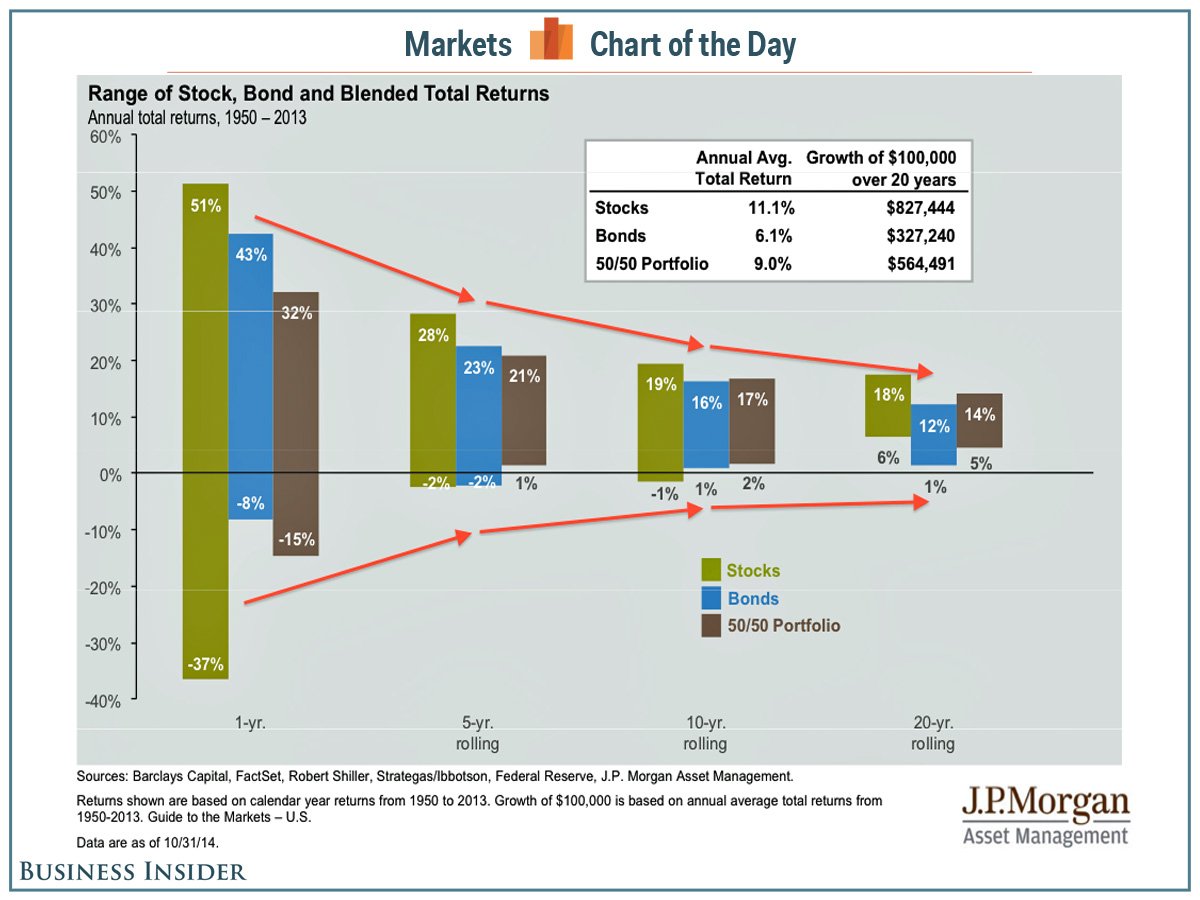
The best long-term investments tend to be companies that can reinvest over and over again at high rates of return. Those high rates of return attract competitors so you must also understand barriers-to-entry. But first study how to calculate incremental returns on capital or marginal returns on invested capital (“MROIC”). There are several links and documents below to help you. The effort is worth it if you can find: WMT_50 Year SRC Chart (up to 2000). WMT had regional economies of scale until it out-grew them.
From John Huber of Base Hit Investing
- Eridon855 says:
Is there a way to calulate return on reinvested earnings?
- John Huber says:
One quick and dirty way is to look at the amount of capital the business has added over a period of time, and compare that to the amount of incremental growth of earnings. Last year Walmart earned $14.7 billion of net income on roughly $125 billion debt and equity capital, or just under 12% return on capital. Not bad, but what we really want to know if we are going to buy Walmart is a) how much of their earnings will they retain and reinvest in the business going forward? and b) what will the return on that reinvested capital be?
10 years ago in fiscal 2006, Walmart earned $11.2 billion on roughly $83 billion of capital, or around 13.5%. But in the subsequent 10 years, they invested roughly $42 billion of additional debt and equity capital ($125b invested in 2016 and $83b invested in 2006), and using that incremental $42 billion they were able to grow earnings by about $3.5 billion (earnings grew from $11.2 billion in 2006 to around $14.7 billion in 2016). So in the past 10 years, Walmart has seen a rather mediocre return on the capital that it has invested during that time (roughly 8%).
We can also look at the last 10 years and see that Walmart has retained roughly 35% of its earnings to reinvest back in the business (the balance has been primarily used for buybacks and dividends). As I’ve mentioned before, a company will see its intrinsic value will compound at a rate that roughly equals the product of its ROIC and its reinvestment rate. So if Walmart can retain 35% of its capital and reinvest that capital at an 8% return, we’d expect a modest growth of intrinsic value of around 3% per year. Stockholders will see total returns higher than that because of dividends, but the value of the enterprise will likely compound at roughly that rate. And we can see that over the previous 10 years, Walmart’s stock has grown around 45% not including dividends. So unless you are banking on an increase in P/E ratios, you’re unlikely to achieve a great result buying a business that can only invest a third of its earnings at 8% returns.
This is a really rough measure, and this back of the envelope method works okay with a large, mature company like Walmart. But what you really want to know is what will the business retain going forward and what will the return be on the capital it retains and reinvests? Of course, there are different ways to measure returns (you might use operating income, net income, free cash flow, etc…) and there are many ways to measure the capital that is employed. But hopefully this is a helpful example from a general point of view.
Calculating Incremental Returns on Capital
- http://basehitinvesting.com/calculating-the-return-on-incremental-capital-investments/ Worth studying this blog and many other posts!
ALSO, read and study these articles:http://basehitinvesting.com/tag/roic/
For extra study go here:
- http://basehitinvesting.com/bhi-library/
- http://www.tankrich.com/2015-46-evaluating-capital-allocation/ not directly related but of interest.
- http://www.tankrich.com/2015-31-value-drivers/ Ditto
- Dale Wettlaufer on ROIC and MROIC
- EconomicModel of ROIC_EVA_WACC
- Owner earnings and Capex
- ROIC and the Networking Industry
- ROIC
—
Reader’s Question
Hi John,
I love the “no hope” strategy for finding ideas. See http://csinvesting.org/2016/06/04/search-process-no-hope-dry-bulk-shipping/
I suppose there is always headline risk with things that have been in multi-year bear markets.
I am curious if you have any thoughts about political consequences of increased isolationist sentiment in the US and Europe? Reply: Actually, the recent sell-off in the shippers this past week (June 17th, 2016) has partially been (I believe) due to Brexit. You always want to look where sentiment is the worst and then try to determine if the price reflects the known news. So on the one hand the rising fears over isolation give me comfort that a lot of bad news is being priced in. Also, if the EU breaks up, why should trade go down? Britain already sells more to the EU than it imports. Switzerland isn’t in the EU and it has one of the strongest economies in Europe. The EU makes no logical economic sense–how can central planning EVER work? Nations have a natural interest to trade with each other since individuals benefit. What Trump says and can do (even if elected) are two separate issues. I really don’t know how to handicap. What I want is terrible news to encourage ship owners not to order new ships and to scrap the ones that they have.
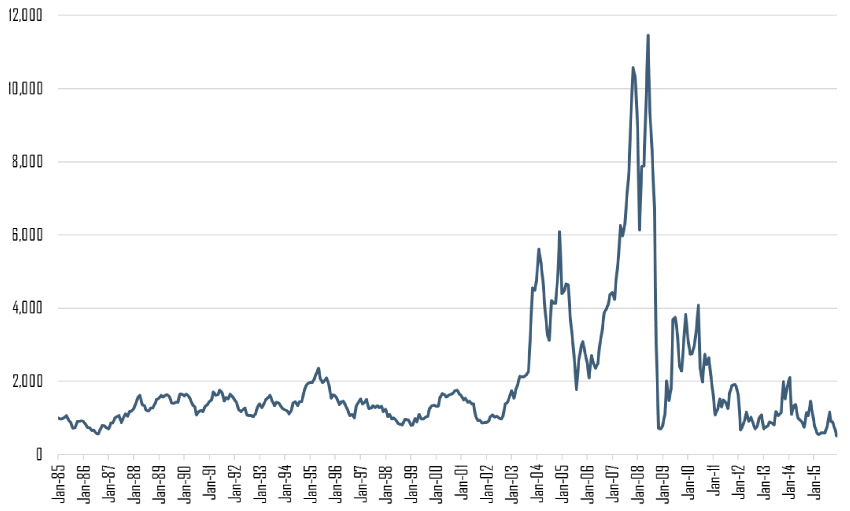
Also curious about your thoughts on the surge in low-cost vessels that came from Chinese ship makers in the last several years. Reply: This has been one of the reasons this shipping cycle has been the worst in forty years. Easy credit/subsidized loans created a boom in Chinese ship builders (See May 7th, 2016 Economist issue and http://www.economist.com/news/leaders/21698240-it-question-when-not-if-real-trouble-will-hit-china-coming-debt-bust. Now some Chinese ship builders are close to bankruptcy. So, yes, this oversupply will make this cycle–already a long one–drag out, but who knows for how long?.
I subscribed to Trade Winds (shipping trade magazine) a couple of years ago, to keep abreast of the industry and try to find when industry sentiment started to pick up. So far, it’s still been abysmal, although this years spike in iron ore was pretty interesting. Especially because Wall Street analysts are still telling everyone iron ore is going lower and this is just a blip. Reply: Wall Street just tells you AFTER the fact or projects the trend/obvious. As one ship owner said (Diana Shipping) said, “The bulk shipping market will turn when no one believes it will turn.”
Ordered the book just now. Really interested to learn more about the industry, and it’s cool that it’s in novel form. I think some of these shippers may start getting close to scrap value pretty soon. Reply: The Shipping Man was an educational and enjoyable read. I may even search for other book like Viking_Raid_Excerpt
Explore:
- https://shippingmanbooks.wordpress.com/2014/01/08/analyst-examines-stealthgas-in-context-of-the-shipping-man/
- https://shippingmanbooks.wordpress.com/ and
- https://www.marinemoney.com/forums/presentations.htm
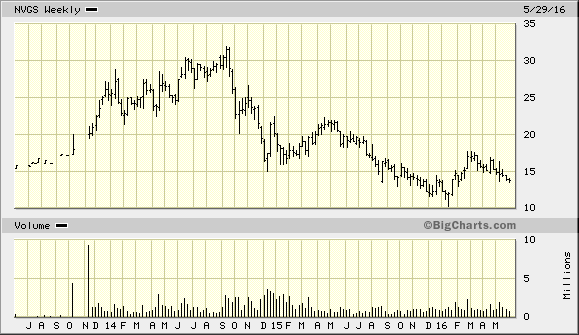
Just remember that the shipping industry has big demarcations. A company like Navigators’ Holdings (an LPG shipper) has different market dynamics than a dry-bulk shipper like Scorpio Bulkers. One shipper operates in more of a oligopoly market than a purely competitive one though both, obviously, are cyclical.
I highly recommend the 800 page opus, Maritime Economics (3rd Edition) by Martin Stopford. If you wish to dig into the shipping industry, then read the annual reports/presentations of several shippers. I have a ways to go to understand this market. The author: https://youtu.be/e2TToPf5iDs
Speculating in shippers is a bit like playing poker. You don’t want the ship owners to start ordering new ships if freight rates start to rise. You want the other owners to disbelieve a sustained rise. When supply is constrained for a few years coupled with a spike in demand, the shipping market explodes like in 2007–no wonder a large supply of ships eventually came into the market and the boom went to bust. The SIZE of the prior boom has led the depth of this bust.


 “I think you have to be very humble about your ability to be smart enough to exploit other people’s stupidity.”
“I think you have to be very humble about your ability to be smart enough to exploit other people’s stupidity.”