The intrinsic value of a company lies entirely in its future–Warren Buffett
All intelligent investing is value investing–acquiring more than you are paying for. You must value the business in order to value the stock.–Charlie Munger
In the old legend the wise men finally boiled down the history of mortal affairs in the single phrase, “This too will pass.” Confronted with a like challenge to distill the secret of sound investment into three words, we venture the motto, “margin of safety.” – Benjamin Graham
Potential Case Study on Growth Capex: HP
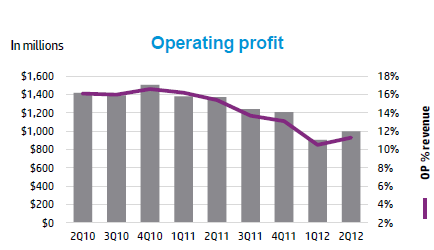
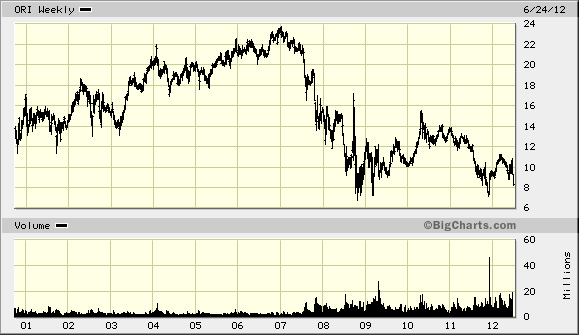
HP paid about $13 billion in 2008 and now announces a 62 percent write-off of its “growth capex” with this $8 billion dollar write-down of acquired Electronic Data Systems (EDS) Goodwill. Are there any lessons here? Note the graph of EDS operating profit below.
History of EDS: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_Data_Systems
Compare technology company acquisitions: http://technology-acquisitions.findthedata.org/
Note 5: Acquisitions (HP 2008 8-K) on Price Paid for EDS
Acquisition of Electronic Data Systems Corporation (“EDS”)
As previously disclosed in its Consolidated Financial Statements for the fiscal year ended October 31, 2008, on August 26, 2008, HP completed its acquisition of EDS. The purchase price for EDS was $13.0 billion, comprised of $12.7 billion cash paid for outstanding common stock, $328 million for the estimated fair value of stock options and restricted stock units assumed, and $36 million for direct transaction costs. Of the total purchase price, a preliminary estimate of $10.5 billion has been allocated to goodwill, $4.5 billion has been allocated to amortizable intangible assets acquired and $2.0 billion has been allocated to net tangible liabilities assumed in connection with the acquisition. HP also expensed $30 million for IPR&D charges.
The merger proxy from 2008 is here:HP Merger with EDS Financial Statements
HP did not pay a low price as you can see from the EDS financial statements above. Acquisitions of different businesses are fraught with peril: integration issues, CEO hubris, size over profits, and buying during the peak of the market (mid-to-late 2007).
I post this as a reminder to return and look more deeply into any lessons I can take away from this transaction. Time, alas, is too short these days to stop and dig in.
Added 5 PM: Differing Opinions in 2008 on the merger
http://seekingalpha.com/article/77186-hp-s-eds-purchase-will-spur-tech-m-a
Hewlett-Packard Co.’s (HPQ) $13.9 billion purchase of IT outsourcer Electronic Data Systems Corp. (EDS) will likely shake up the sluggish high-tech M&A climate on many fronts, establishing HP as a successful acquirer of multibillion dollar businesses that could eventually pursue other large targets, while potentially spurring rival IBM Corp. (IBM) to explore purchases to solidify its shrinking lead in IT services.
As the largest high-tech acquisition so far this year, HP’s $25-per-share purchase of Plano, Texas-based EDS may also wake up other high-tech companies to the compelling values to be had now that stock prices are low, analysts said.
“In a recessionary climate, the reality is that many of these properties are pretty cheap,” said Rob Enderle, principal analyst at Enderle Group in San Jose, Calif. Enderle said larger acquisitions that emphasize acquiring people become particularly attractive in a weak economy, because a soft job market makes it more likely the target’s employees would stay, minimizing one key integration challenge.
HP’s $25 per share purchase price represents a 32.9% premium EDS’ share price on May 9, but it is still considerably cheaper than EDS’ market capitalization over much of the past year, and significantly below EDS’ 52-week high of $29.13 per share. Coming on the heels of Microsoft Corp.’s (MSFT) abandoned $47.5 billion bid for Yahoo! Inc. (YHOO), this message about the values in the high-tech sector resonates.
—
Opinion: HP’s acquisition of EDS leaves questions unanswered
http://www.computerweekly.com/opinion/Opinion-HPs-acquisition-of-EDS-leaves-questions-unanswered
Although Hewlett-Packard’s acquisition of EDS was expected, the premium that HP paid was unexpected, and potentially unwarranted, given EDS’s recent track-record and a depressed outsourcing market. This sentiment was reflected in the market’s reaction, which wiped £8bn off HP’s capitalisation – more the than £7bn HP paid for EDS. Not an auspicious start.
One major concern now has to be that HP has enjoyed great growth through non-exclusive partnering with rivals worldwide to secure business. Such partnering will now essentially come to a halt or be severely constrained. This comes on top of the huge and immediate task of integrating two very different business cultures. HP’s young and energetic “cut and thrust” team is now under the control of EDS chairman, president and chief executive officer, Ronald A. Rittenmeyer. This does not bode well for transferring staff, as EDS is far more formal, structured business.
HP’s “cheque-book funding” will allow EDS to tender for more US and UK government work where balance sheet considerations play an important part in the larger deal constructs. However, EDS’s margins are far lower than HP’s – group CEO, Mark Hurd, will demand better ratios in line with investment community demands and that HP has, up to now, a record of achieving.
Neither HP nor EDS has a serious business consultancy arm, and EDS squandered the talents of AT Kearney before selling it several years ago. The new company offers “customers the broadest, most competitive portfolio of products and services in the industry,” says Mark Hurd. Perhaps he forgets that clients favour multi-sourcing precisely to gain specialist skills and, importantly, innovation. Being the number two outsourcer by revenue globally will not help sustain this position if serious business consultancy is lacking. Is there another plan afoot to mitigate this structural and strategic short-fall? Given the decision delays in securing the EDS deal, I suspect not.
Infrastructure consolidation, virtualisation and greening is a big boys’ “scale is everything” game and one for those with deep pockets too. The new HP can win huge revenues in this end of the market, however it will be at the expense of profitability.
It was therefore hugely significant to note that no mention has been made of “deal synergies”. With a combined total of 210,000 staff, one would have expected 20% to be saved almost immediately. Integration of technologies would normally be expected too. This usually results in 10% in immediate savings, which could increase to 15% over time. Increased buying power would add 2% to 8% depending on the product or service being bought. None of this has been mentioned.
All of these savings should run to hundreds of millions of pounds. You only get one chance to impress clients, analysts, intermediaries and, most importantly, the market-makers and institutional investors.
The time to have captured the market’s mood and imagination was at the announcement, it has now passed Hurd by. Only results will count now.
This deal is likely to be the catalyst for additional outsourcing consolidation with Atos Origin, CapGemini and even CSC. Will the cash-rich Indian offshored services providers finally make a move? These are truly perplexing times for new and existing clients of outsourcing.
By Robert Morgan, director of Hamilton Bailey