The First Economist

Hayek’s Road to Serfdom
A Reader’s Digest Version–thirty pages–of Hayek’s Road to Serfdom, plus cartoons. Hayek and Mises both predicted the inevitable collapse of socialism and fascism. http://www.cblpi.org/ftp/Econ/RoadtoSerfdom
_ReadersDigest_and_Cartoon_Versions.pdf
Quantitative Easing explained in a cartoon video. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PTUY16CkS-k About five million viewers have watched this video of two bears (dogs?) asking simple questions about monetary policy. The theory at issue here is Keynesianism which assumes that stimuli from government, a category that includes QE2 (Quant. Easing for the second time), are beneficial. Really? Why? If economics can neither be explained in plain English nor understood then it’s probably bunk.
For a Future Case Study on Moats
http://www.nytimes.com/2011/12/17/business/at-amazon-jeff-bezos-talks-long-term-and-means-it.html?_r=2&ref=jamesbstewart&pagewanted=print
Amazon Says Long Term And Means It By JAMES B. STEWART
In 1997, the year Amazon.com went public, its chief executive, Jeff Bezos, issued a manifesto: “It’s all about the long term,” he said. He warned shareholders “we may make decisions and weigh tradeoffs differently than some companies” and urged them to make sure that a long-term approach “is consistent with your investment policy.” Amazon’s management and employees “are working to build something important, something that matters to our customers, something that we can tell our grandchildren about,” he added.
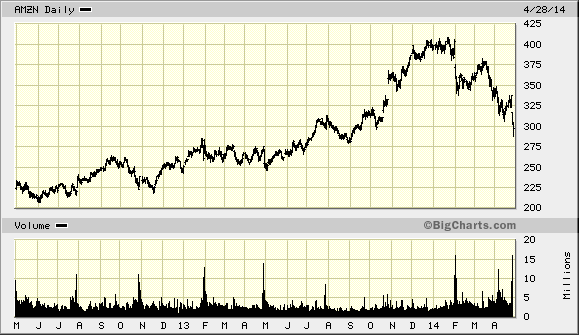
But shareholders seem never to have gotten the message. In October, when Amazon reported strong third-quarter revenue growth and earnings that were pretty much what the company had predicted, but indicated it would be spending more to support continued growth, investors hammered its stock. Amazon shares dropped nearly $30, or 13 percent, to $198 a share in just one day, Oct. 25. This week they were trading even lower, at $181.
Over the years, Amazon shares have been periodically buffeted by short-term results that seem to have disappointed investors. “The stock has been bumpy,” a Morgan Stanley analyst, Scott Devitt, told me this week. “Investor trust seems to go in cycles.”
The notion that public companies should maximize shareholder value by managing for the long term is pretty much gospel among good-governance proponents and management experts. Jack Welch advanced the concept in a seminal 1981 speech at the Pierre Hotel in New York and elaborated on it in subsequent books and articles while running General Electric, when G.E. was widely lauded as the best-managed company in the country. It has been especially championed in Silicon Valley, where technology companies like Google have openly scorned Wall Street analysts and their obsession with quarterly estimates and results by refusing to issue earnings guidance.
Amazon, in particular, has been true to its word to manage for the long term. It remains one of the world’s leading growth companies and its stock has soared 12,200 percent since its public offering. In late October it reported quarterly revenue growth of 44 percent to almost $11 billion, which came on the heels of 80 percent growth a year ago. “We’re seeing the best growth which we’ve seen since 2000, meaning in 2010 and so far over the past 12 months ending September,” the chief financial officer, Thomas Szkutak, told investors in October. But operating earnings fell sharply to $79 million. While that was in line with most estimates, Amazon offered a forecast for the fourth quarter in which it said it might lose as much as $200 million or earn as much as $250 million, and even the high end would represent a 47 percent drop.
The reason Amazon is earning so little while selling so much is that it is spending so much on long-term growth. It’s opening 17 new fulfillment centers — airport hangar-size storage and shipping facilities — this year and aggressively cutting prices. Its profit margin for the quarter was just 2.4 percent, and it said it might be zero for the fourth quarter. (By comparison, Wal-Mart’s margins are 6 percent on revenue of $440 billion. )
Amazon seems to be taking customer focus to new levels, willing to run its ever-bigger global business while earning little or nothing in return. To the dismay of some, Mr. Bezos even takes a long-term view of price cuts. “With rare exceptions, the volume increase in the short term is never enough to pay for the price decrease,” he told shareholders in 2005. But that kind of thinking, he added, is “short term. We can estimate what a price reduction will do this week and this quarter. But we cannot numerically estimate the effect that consistently lowering prices will have on our business over five years or 10 years or more.” Selling at low prices may undercut profits, but they create “a virtuous cycle that leads over the long term to a much larger dollar amount of free cash flow, and thereby to a much more valuable Amazon.com,” Mr. Bezos said.
Amazon has done little to dampen speculation that it is selling its revamped Kindle e-reader devices and its recently introduced Fire tablet at a loss. Amazon simply doesn’t think like most other companies. When “we think about the economics of the Kindle business, we think about the totality,” Mr. Szkutak said. “We think of the lifetime value of those devices. So we’re not just thinking about the economics of the device and the accessories. We’re thinking about the content.” In other words, profits will come down the road when Kindle users buy content through Amazon.
“If everything you do needs to work on a three-year time horizon, then you’re competing against a lot of people,” Mr. Bezos told reporter Steve Levy last month in an interview in Wired. “But if you’re willing to invest on a seven-year time horizon, you’re now competing against a fraction of those people, because very few companies are willing to do that. Just by lengthening the time horizon, you can engage in endeavors that you could never otherwise pursue. At Amazon we like things to work in five to seven years. We’re willing to plant seeds, let them grow—and we’re very stubborn.”
Whatever they might say about long-term shareholder value, this is simply too much for many of today’s investors, many of whom are hedge funds, pension funds and institutions who measure their results — and earn their pay — based on quarterly benchmarks. “If you look at the average length of ownership of a stock, the period is declining,” Mr. Devitt said. “Amazon is marching to a different drumbeat, which is long term. Are they doing the right thing? Absolutely. Amazon is growing at twice the rate of e-commerce as a whole, which is growing five times faster than retail over all. Amazon is bypassing margins and profits for growth.”
For Amazon, long-term growth confers two major benefits: the kind of economies of scale enjoyed by Wal-Mart and eliminating or weakening competitors. The book retailer Borders has been forced out of business and a rival, Barnes & Noble, is struggling. Best Buy, the electronics retailer, reported this week that earnings plunged 29 percent, despite higher revenue and a surge of Black Friday sales, because the chain had to cut prices and offer free shipping to compete with Amazon. Amazon inflamed many competitors this holiday season by offering extra discounts to shoppers who took mobile devices into stores and then used them to compare prices and order from Amazon.
The revamped Kindle line and especially the new Fire tablet illustrate Amazon’s long-term strategy. “Amazon has much greater ambitions than near-term profits or margins,” Ken Sena, an Evercore analyst, said.
“Some people are griping that the Fire is sub-par,” Mr. Sena continued. “It’s not an iPad. And some investors are confused. Why would they give it away, even lose money on it? But getting it into as many hands as possible is important to them. They’ll use it to drive higher physical and digital good sales on their site. And these devices also bring Amazon deeper into the local retail opportunity, not to mention the app marketplace potential that exists. Media sales on the device are just the beginning. I think Amazon understands all these components.”
The Fire “isn’t meant to be another iPad,” Mr. Devitt noted. “It’s a device to sell Amazon content. All indications are it’s a success. It’s the most gifted item on Amazon. It’s too soon to tell, but it seems more promising than it’s getting credit for.” This week Amazon said it had sold more than a million Kindles a week for the last three weeks.
Nearly 15 years after Amazon’s public offering, it’s safe to say that Mr. Bezos and his colleagues have realized their goal of creating a company to tell their grandchildren about. But one of these days Amazon has to deliver on its promise of higher margins and profits, however long term that may turn out to be. “To many investors, long term is a year,” Mr. Devitt said. “For Bezos, he’s looking at a 10- to 20-year time line. When he says long term, he means 2020 or 2030.”
Now from http://ycharts.com/ Amazon: Free Shipping and Low Prices Don’t Add Up To a Moat By Jeff Bailey
The smartest guy in financial journalism, James B. Stewart, earlier this month in his Saturday New York Times column, praised Amazon (AMZN) for taking the long view in building its business and criticized the company’s critics for failing to appreciate the company’s steadfastness. (See above.)
Amazon revenue continues to rise spectacularly. Its profits, however, have fallen, as margins are squeezed by aggressive product pricing and surging use of the company’s popular free-shipping option. So, the question seems to be, will those strategies help Amazon build what Warren Buffett would call a moat – a protective fortress around its business that long-term allows it to reap substantial profits and build value?
Stewart, author of several fabulous business books, including “Den of Thieves,” about the late-1980s Wall Street scandals, and a Pulitzer Prize winner for his work at the Wall Street Journal, is such a well-regarded thinker about companies that we at YCharts were forced to stop and consider his point of view; he’s not just another pro-Amazon tout.
We have regularly written that we view Amazon as overvalued and have marveled at how its recent growth has made it less profitable, not more so.
The critics have certainly influenced Amazon’s share price in recent months.
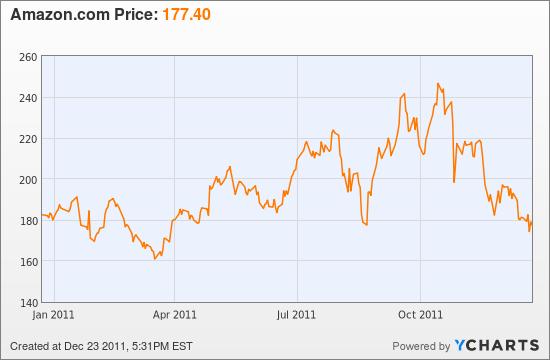
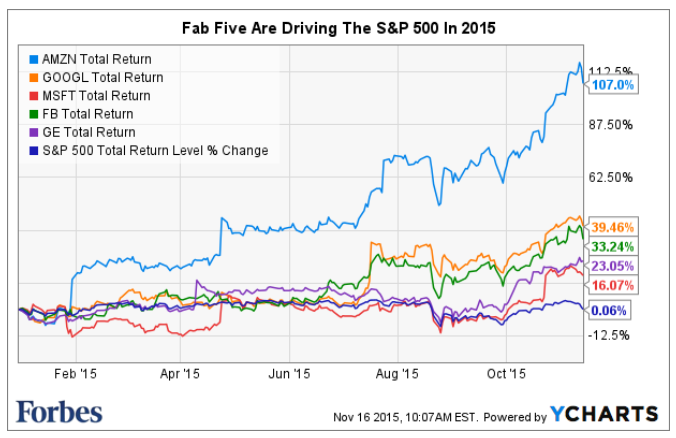
Amazon.com Stock Chart by YCharts
Yet the PE remains in the 90s, and this for a company with a plunging and razor-thin profit margin.
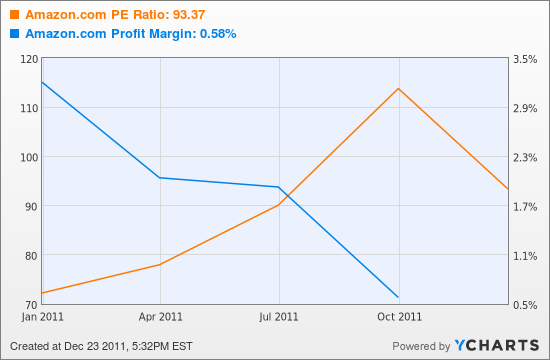
Amazon.com PE Ratio Chart by YCharts
Stewart’s admiration of Amazon certainly makes sense if you’re an Amazon customer. The service is wonderful, and like so many American shoppers during this holiday season we have ventured into actual stores very few times because shopping online – from Amazon and its many imitators – is so much easier. That change in consumer behavior seems to suggest a moat is forming. But does the moat encircle Amazon protectively, or is it instead a moat encircling bricks-and-mortar retailers into a market-share-losing ghetto?
The brutal price-comparison ethic Amazon unleashed on the book business years ago helped it take huge market share. But it also rendered the book business less profitable for all players. And as that ethic unfolds across product categories – aided most recently by Amazon’s Price Check app – results at Amazon and Best Buy (BBY) would suggest the greater transparency on pricing is helping consumers, but not so much retailers.
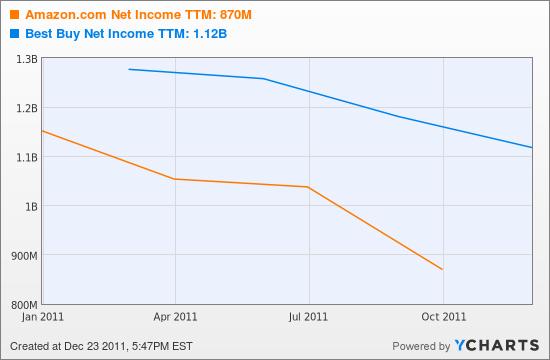
Running Borders out of business, sadly for Amazon and other booksellers, didn’t make the book business more profitable again. Rather, the pricing model Amazon brought to the market seems to have rendered book retailing a crummier business. And it’s also unlikely that consumer electronics and the other categories Amazon is transforming will, once a few large competitors go bust, miraculously become more profitable. There isn’t a shortage of players in any of these markets and the consumer behavior Amazon helped spur – constant price shopping, demanding free or reduced-priced shipping – would seem impossible to reverse.
The Wall Street Journal recently noted the toll free shipping is taking on retailers’ profits. The Journal, noting Amazon’s shrinking margins, said, “Free shipping has likely played a meaningful role in this, although the company hasn’t detailed the cost.”
Actually, Amazon does detail the cost in its 10-K filings (page 26). Its net shipping costs – total shipping costs minus what Amazon collects from customers for shipping – totaled $1.39 billion in 2010, up 63% from $849 million the prior year. Total sales were only growing by 40%. So net shipping costs were equal to 4% of sales in 2010, versus 3.4% in 2009. That trend may have accelerated during 2011, and could largely explain why profits have fallen.
The strategy Stewart lauds is doing a bang-up job of boosting revenue. And consumers love Amazon’s service. But it’s hard to see how the company is going to fatten its margins when competition remains fierce; consumers have been taught to demand low-low prices (and free shipping); and beyond elegant technology, Amazon’s main tools for attracting consumers are both margin killers — low-low prices and free shipping.
Certainly the Kindle is an attempt to build a moat around Amazon’s book business. Selling the devices at what has been reported as a loss suggests the company sees future payoff from Kindle-owning consumers downloading their reading (no shipping expense here) exclusively from Amazon. But in the more general merchandise categories that increasingly make up Amazon’s sales, it’s hard to see how to insert such a loyalty device.
Stewart’s argument seems in part based on the notion that, forgoing current profits, Amazon must be managing for the long term. But if your very pricey stock is reliant on spectacular revenue growth, a cynic might reason that a strategy of adding sales — even if they’re increasingly less profitable (or money-losing) – appears short-term and somewhat desperate.
Amazon management is smart, as is Jim Stewart, and investors could be inviting ruin by shorting Amazon shares. But to us, the company hasn’t made a persuasive case that it’s building a moat – just that it’s delivering great service and selling stuff cheaper than the next guy. End.
Let’s revisit our study of whether Amazon has a competitive advantage or not after we finish our study of Competition Demystified (in the VALUE VAULT).